Lifecycle of an Enbridge pipeline
With proper design, construction, operation and maintenance, pipelines have a very long life.
At Enbridge, the safety of people, and protection of the environment, is our top priority throughout the entire pipeline lifecycle. Explore that lifecycle below with a step-by-step interactive journey.
PLEASE NOTE: The objects and terrain presented in this experience are not to scale.


Design and Construction
Safety and reliability are built into Enbridge’s energy infrastructure before, during and after the construction phase.We take care to limit our footprint, and actively manage potential effects on communities and the environment, as we build our pipeline projects.
Where possible, we use existing access routes to and from construction sites, minimize temporary workspace and curtail ground disturbance.
Screening and planning
It can take seven to nine years to build a pipeline. But it all begins with a need for energy.
Everyone relies on energy. Whether it’s for cooking a hot meal, taking a warm shower, charging our phones, heating our homes, or filling our tanks at the pump, each of us relies on energy.
The peaks and demands of the need for energy can change year over year. To meet the needs of the communities, refineries, businesses, schools, hospitals, and manufacturers, we assess both the supply and demand for oil and energy over the long term, and carefully calculate the economic feasibility of a particular pipeline.
Start of dialog
The Planning Process
The planning process
We have an unwavering commitment to safety, reliability and meeting or exceeding regulatory standards. True commitment, though, is more than thoughts and words. That’s why we invest consistently into actions that clearly demonstrate our focus on respecting communities and the environment.
Community engagement
We live here. We work here. We raise families here. From meetings to presentations to our community investment program, we are part of the community.
We engage in a variety of ways, including open houses, presentations to civic and business groups, roundtable discussions with municipalities, meetings with landowners and Indigenous communities, coffee talks and personal interactions.
Consulting with Indigenous groups
Reflecting our commitment to stakeholder collaboration, Enbridge provides Indigenous and Native American communities training, employment and meaningful opportunities that help support their businesses. We also consult with Indigenous and Native American groups about the feasibility of rerouting pipelines around sensitive corridors.
Route planning considerations
We plan our projects with great care and respect to the communities and environment. To help minimize our environmental footprint, we use pre-existing utility corridors where possible. We also comply with all environmental regulations and permits and seek oversight from trained, experienced environmental inspectors and resource specialists.
Discussions with government agencies
We work continuously with regulatory agencies and build environmental evaluations into construction planning.
The U.S. and Canada have had pipeline rules and guidelines in place for decades, resulting in two of the most highly regulated, and safest, pipeline industry environments in the world.
Depending on the project, we may use environmental field survey crews to evaluate and potentially reroute around environmentally sensitive areas.
Wildlife protection strategies include wildlife baseline studies, remote camera monitoring and winter track surveys.
Approval through regulatory agencies
Often, a pipeline project involves seeking and gathering input from more than 40 agencies across federal, regional, state/provincial and local levels. We submit an application to the appropriate agency (or agencies) to initiate the regulatory review process.
End of dialog
Design and construction
Safety and reliability are built into Enbridge’s energy infrastructure before, during and after the construction phase.
We take care to manage potential effects on communities and the environment, and limit our footprint, as we build our pipeline projects to safely deliver the energy that fuels everyone’s quality of life.
This downloadable, printable infographic details the safety and reliability that are built into Enbridge's energy infrastructure--before, during and after the construction phase.
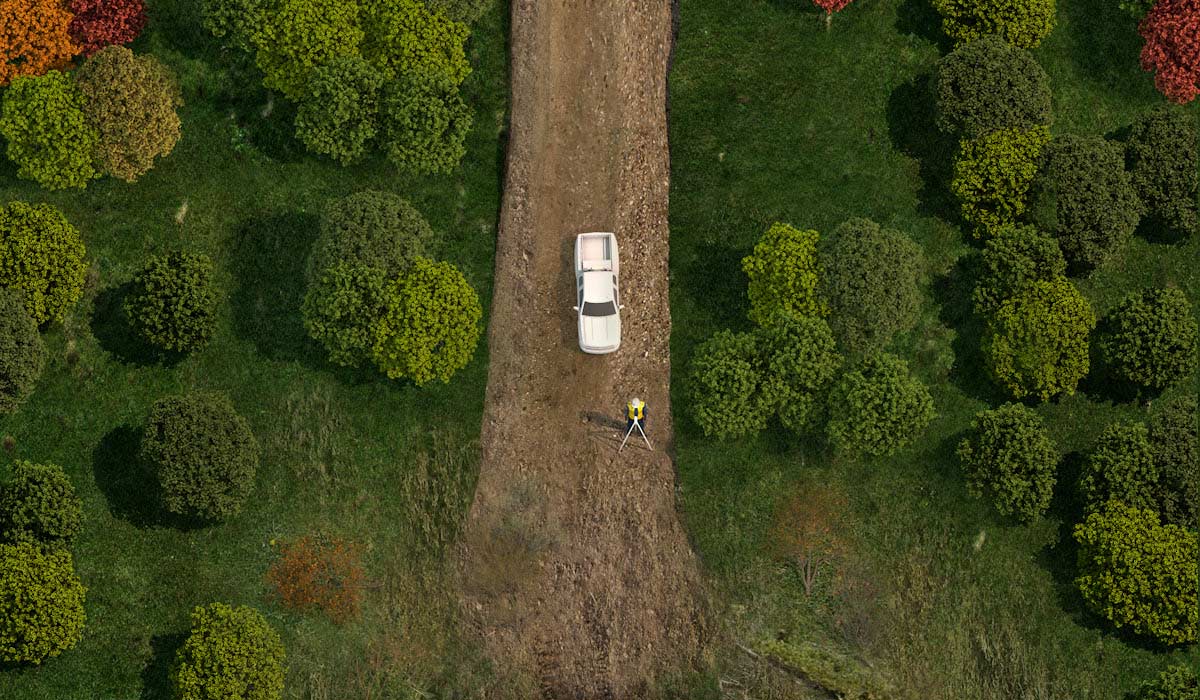


Field surveys and staking
Field surveys are conducted along the proposed right-of-way (ROW) to understand environmental, developmental and local issues.
Once the route is final, the location is marked with stakes.
Field surveys and staking
To understand environmental, developmental and local issues, we conduct field surveys along the proposed right-of-way (ROW). Once the route is final, we mark the location with stakes.
Learn more about pipeline study corridors, and the surveying and staking process.
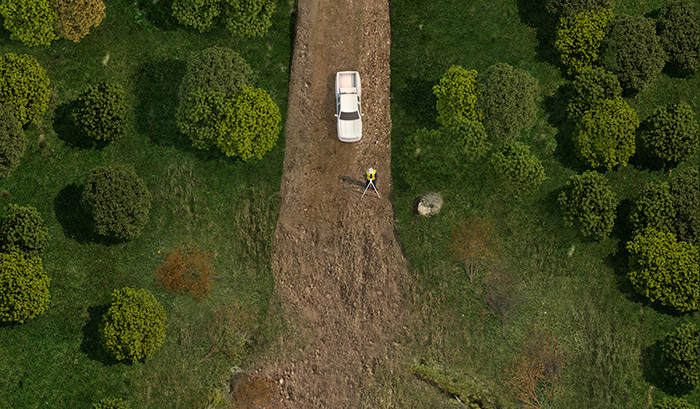


Working with Landowners
We establish project-specific biosecurity plans with the help of landowners, including making sure all of our equipment is clean and free of weeds, soil and debris.
We take measures to control and contain weeds and soil-borne pathogens, based on the level of risk at the construction site.
Clearing
To prepare for construction, crews mulch and/or clear and salvage trees, where warranted, along the ROW and temporary workspace.
Stripping and storing topsoil
We take careful consideration when removing topsoil from the ROW. For biosecurity reasons, we take extra care in agricultural areas to separate and store the topsoil and subsoil so they don’t mix.Working with landowners
We establish project-specific biosecurity plans with the help of landowners, and that includes ensuring all of our equipment is clean and free of weeds, soil and debris.
We take measures to control and contain weeds and soil-borne pathogens, based on the level of risk at the construction site.
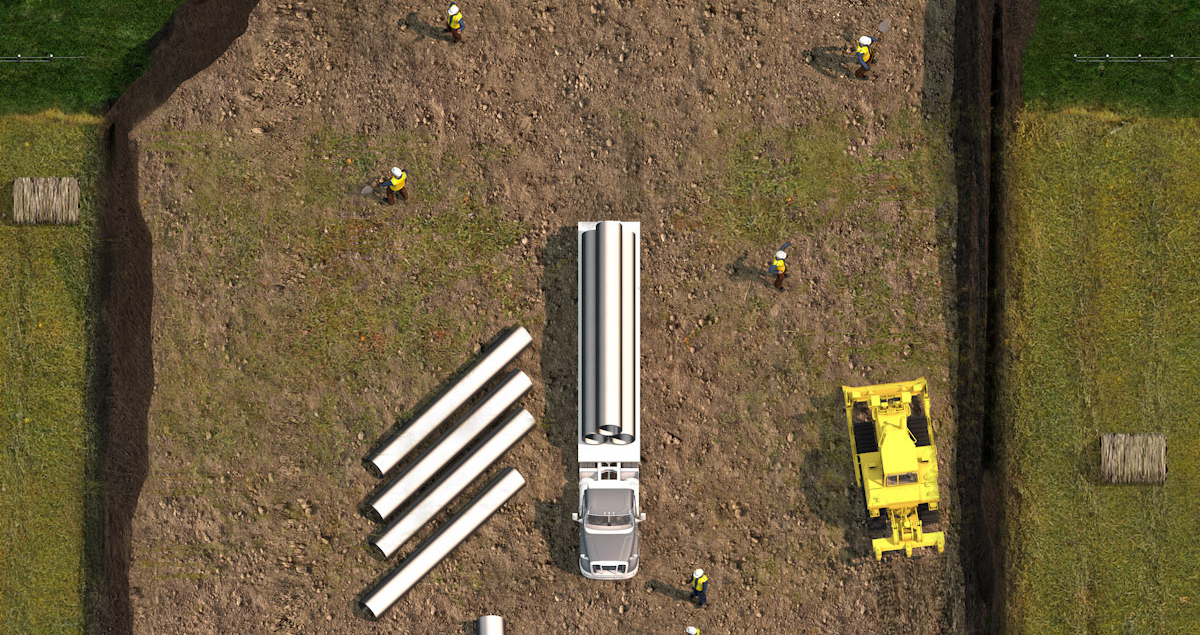
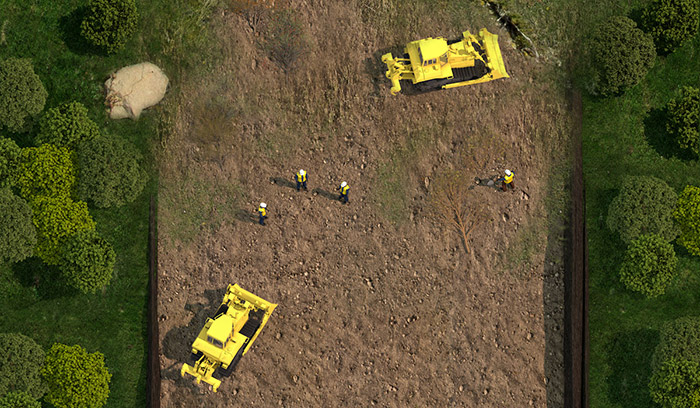


Grading
Once topsoil has been stripped and stored to meet specifications, the subsoil along the ROW is graded to enable a safe pipeline installation.
Grading
Once workers strip and store topsoil to meet specifications, they grade the subsoil along the ROW to help enable a safe pipeline installation.
Pipeline Steel
The heart of our business is the pipe in the ground. Enbridge's demands for pipeline steel exceed industry standards, and we select, inspect and test our line pipe before it’s used in construction.
Our pipe steel itself is made of 96% recycled metal. This alloy is not only a greener product, but also represents excellent chemistry for line pipe.
Weld quality in the pipe mill is examined by the manufacturer using automated ultrasonic devices, and Enbridge inspectors audit those results.
Stringing
Crews re-stake the center of the trench, and place (or “string out”) sections of the pipe along the ROW.
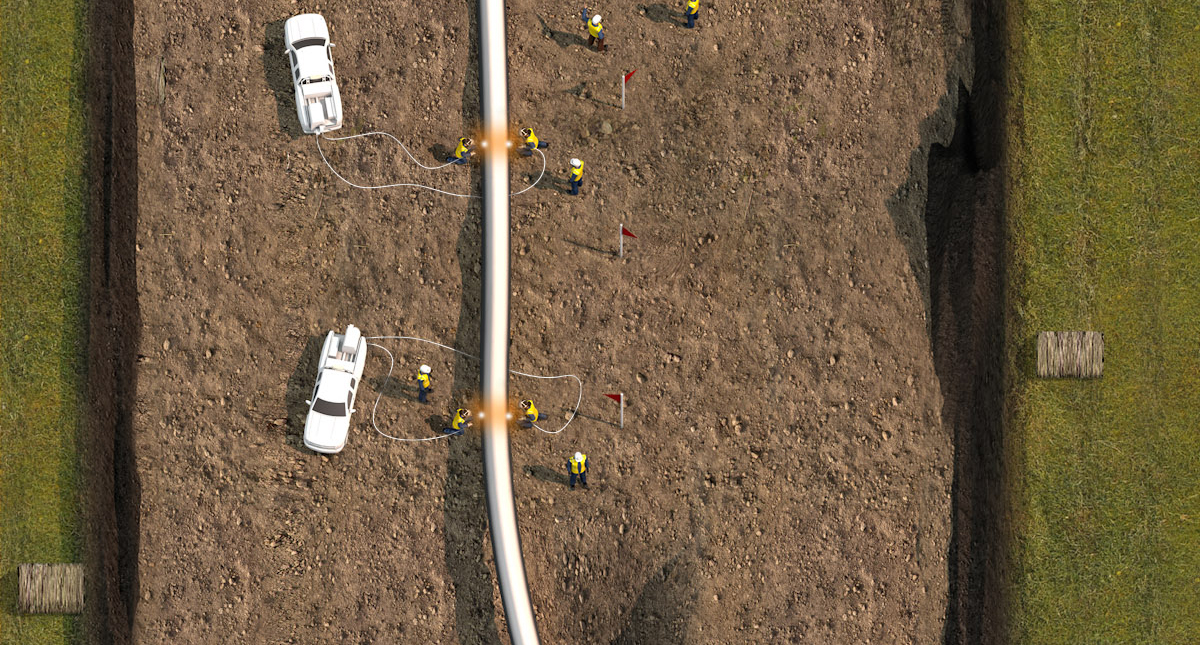


Bending
Crews bend the sections of pipe to match engineering specifications and follow the contours of the land.
Welding
The pipe is welded into sections, and eventually one long segment, using pipe that’s been carefully selected and tested. Each weld is inspected via either X-ray or ultrasound technology.
Coating
The entire segment of pipe, including weld joints, is coated with a robust corrosion inhibitor.
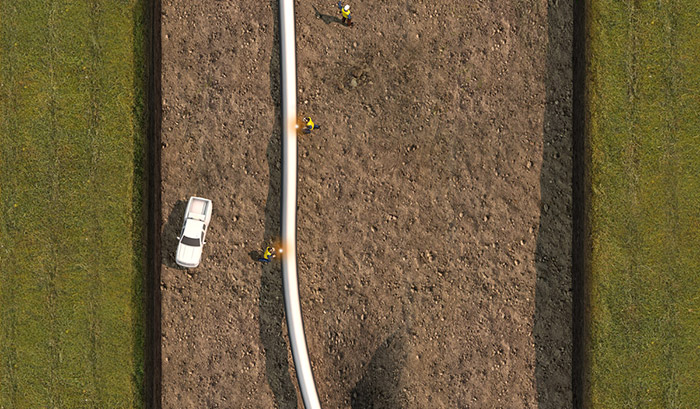
Bending
Crews bend the sections of pipe to match engineering specifications and follow the contours of the land.
Welding
Using pipe carefully selected and tested, workers weld the pipe into sections—and eventually one long segment. They inspect each weld with either X-ray or ultrasound technology.
See our infographic on the welding process Enbridge follows to keep our pipes strong and healthy.
Coating
The entire segment of pipe, including weld joints, is coated with a robust corrosion inhibitor.
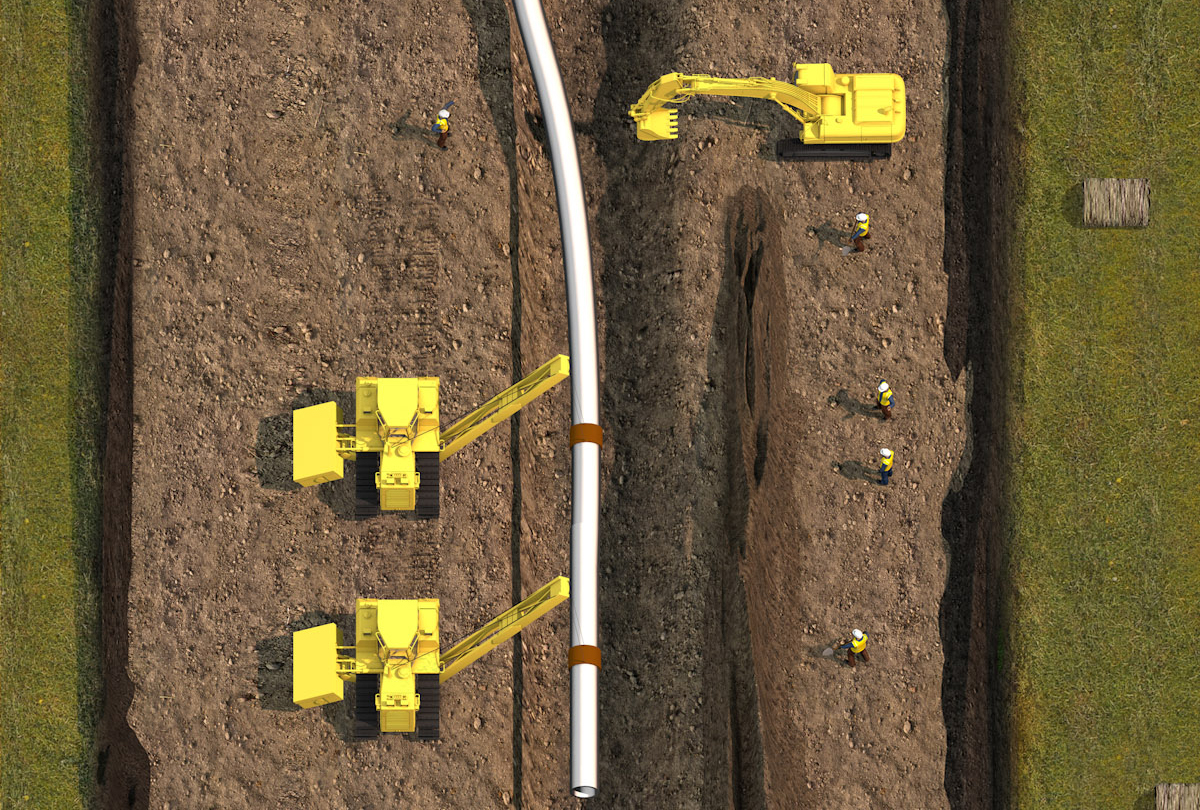


Lowering-in
Using multiple sidebooms, or cranes, the pipe is lowered into the trench.
Trenching
Crews use backhoes or wheel ditchers to dig the pipeline trench.
Trenching
Crews use backhoes or wheel ditchers to dig the pipeline trench.
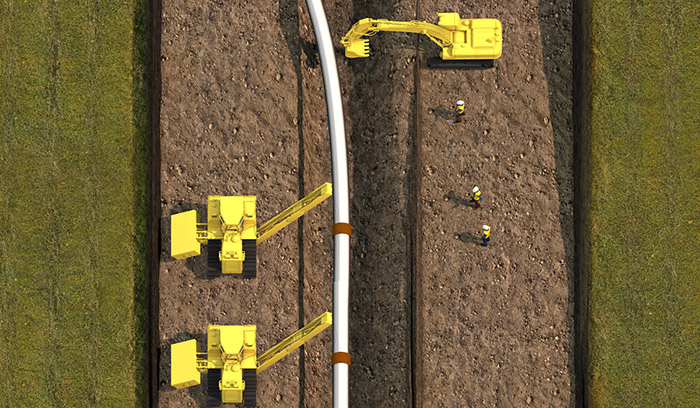
Lowering-in
Using multiple sidebooms or cranes, the pipe is lowered into the trench.
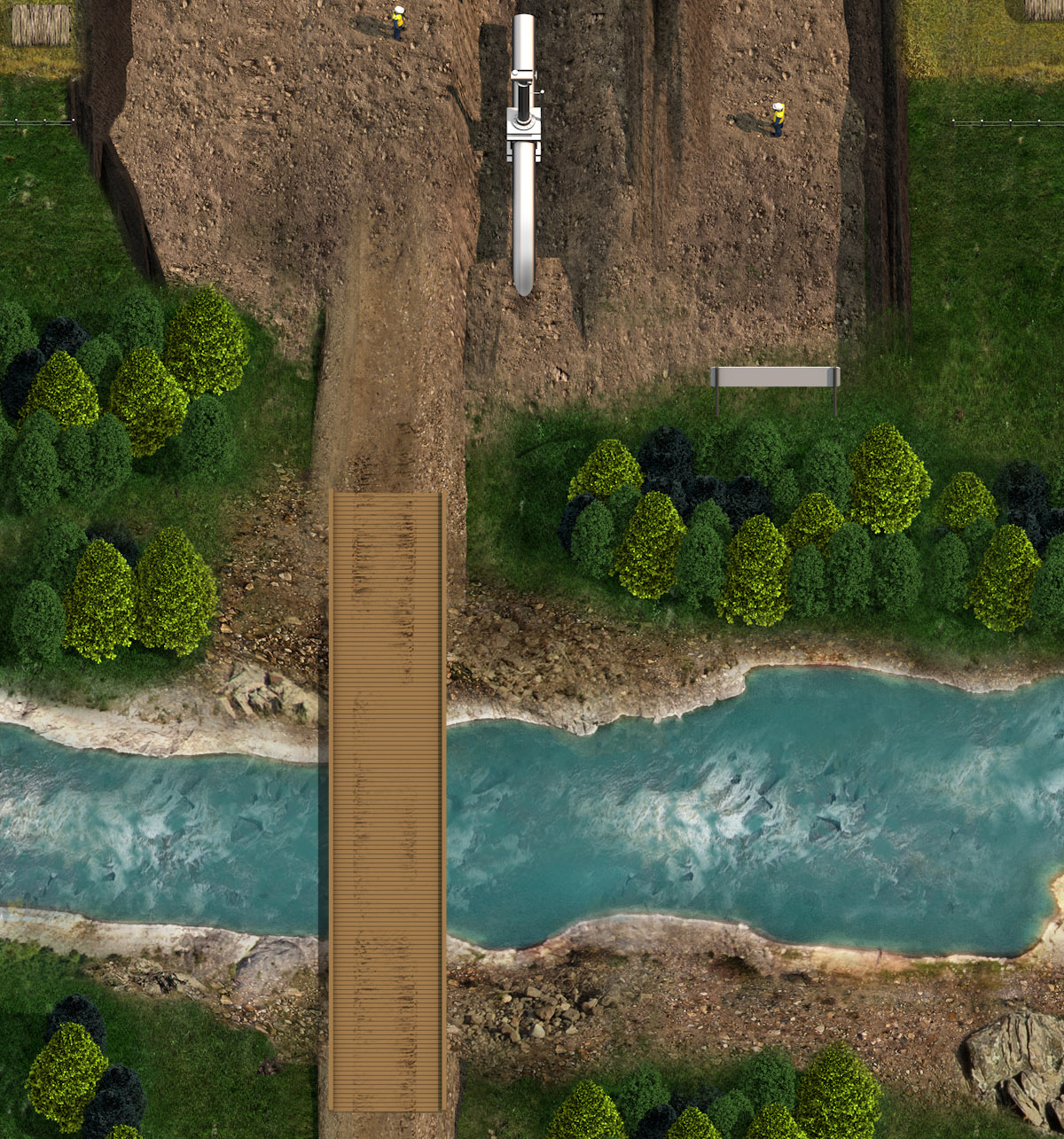
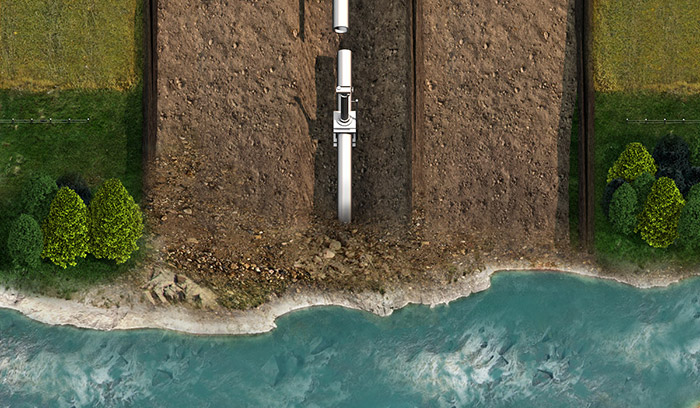


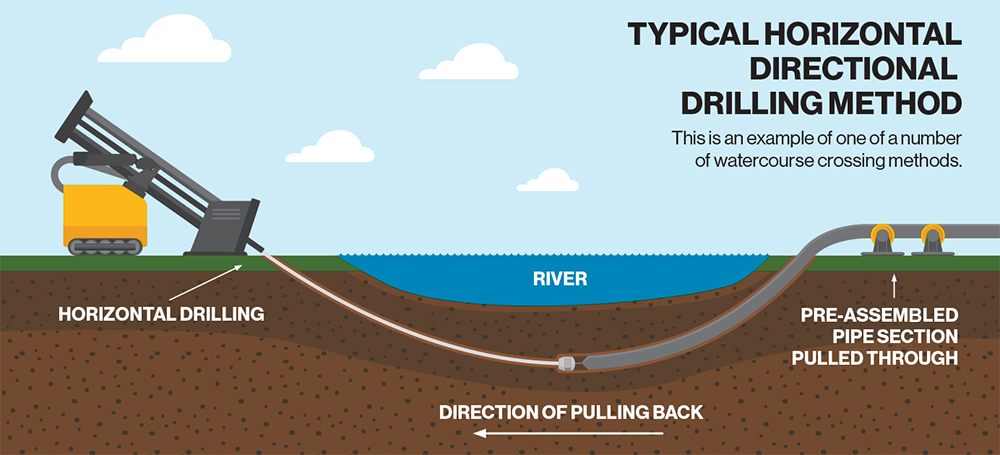
River crossings
Horizontal directional drilling (HDD) technology is deployed to lay pipelines beneath large rivers or sensitive crossings.
ALSO SEE: World's longest HDD project under Mississippi River a 'mind-boggling' feat of engineering
Remotely controlled isolation valves
Isolation valves are used to control or halt the flow of crude oil and other liquids, and represent an invaluable piece of safety equipment on a pipeline system.
We place remotely controlled isolation valves at strategic locations along our pipeline network to minimize potential incidents.
Enbridge's pipeline control center staff, who monitor our pipeline system 24/7/365, can close an isolation valve immediately upon detection of a problem, with full closure within three minutes of activation.
Learn more about Enbridge’s Intelligent Valve Placement (IVP) methodology.
River crossings
In the case of large rivers or certain sensitive crossings, Enbridge uses horizontal directional drilling (HDD) technology when possible to install underground pipelines.
HDD minimizes impact on landowners, communities and the environment, as well as on sensitive habitats and other areas.
ALSO SEE: HDD fact sheet
ALSO SEE: HDD video; Going deep to minimize impact
ALSO SEE: St. Clair River HDD Project for Line 5 carried out with 'textbook execution'
ALSO SEE: World's longest HDD project under Mississippi River a 'mind-boggling' feat of engineering
Start of dialog
See HDD diagram
End of dialog


Backfilling
The trench is carefully backfilled and compacted with subsoil.
Safety and the environment.
This downloadable, printable infographic details the safety and reliability that are built into Enbridge's energy infrastructure--before, during and after the construction phase.
Backfilling
The trench is carefully backfilled and compacted with subsoil.
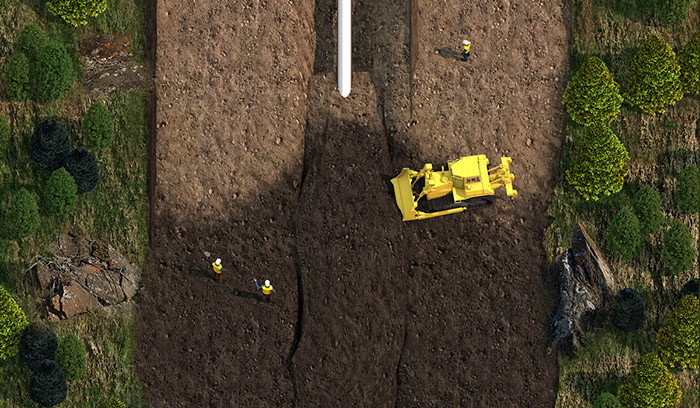


Hydrostatic Testing
Each section of pipe is filled with water and subjected to extreme operating pressures to ensure the strength of the pipe and welds.
LEARN MORE
Cleanup and Reclamation
The ROW is restored to its original condition. Topsoil is replaced and reseeded; other restoration methods include tree planting and environmental monitoring.
Hydrostatic testing
To help confirm the strength of the pipe and welds is sufficient to operate safely, we fill each section of pipe with water and test the sections under extreme operating pressures.
LEARN MORE
Cleanup and restoration
Workers restore the ROW as close as possible to its original condition. They replace topsoil and reseed; other restoration methods include tree planting and environmental monitoring.
This process is known as restoration in the U.S., and reclamation in Canada. Learn more about the process here.

Operations and Maintenance
Once a pipeline enters service, it enjoys a very long life, through safe operations,
prevention, monitoring and maintenance activities. We work hard to meet or exceed
the strict safety and reliability standards enforced in the United States and Canada.
Operations and maintenance
Through safe operations, prevention, monitoring and maintenance activities,
pipelines generally enjoy a very long lifespan. We work hard to meet or exceed federal safety and reliability
standards, which help provide a secure, reliable energy source to fuel North Americans’ quality of life.
LEARN MORE
Maintaining pipeline fitness
Preventative maintenance digs are an important part of keeping our pipelines healthy and fit for purpose.
When our state-of-the-art in-line inspection (ILI) tools, using ultrasound or magnetic flux leakage (MFL) technology, find something that requires a closer look, we excavate the pipe at that location so we can examine it and make any necessary repairs.
Sometimes we find that no repair is required, but each of these preventative maintenance digs adds to our overall knowledge about the line’s condition.


Decommissioning
Landowners are not responsible for Enbridge's decommissioned or deactivated pipelines. We are—forever.
View our Decommissioning PDFSafety
Now that you've explored what we do to safely plan, build, operate and maintain our pipelines, you may want to explore all of the ways Enbridge works to ensure safety for our communities across our facilities and operations.
LEARN MOREDeactivation (U.S.)/Decommissioning (Canada)
Landowners are not responsible for our deactivated/decommissioned pipelines. When we deactivate/decommission a pipeline, we remain responsible, and we adhere to all associated regulatory requirements.
Learn more about deactivation Learn more about decommissioningOur responsibility
We remove any oil from the line, wipe and clean the walls, and physically disconnect the pipeline from our network.
Continuous monitoring
We continue to monitor deactivated/decommissioned pipelines, just as we do with active pipelines. This includes:
- Cathodic protection to curb corrosion
- Maintaining the corridor, signage and contact info
- Maintaining the pipeline’s profile for Call/Click Before You Dig programs
Minimizing impacts
Deactivated/decommissioned pipelines are left in place to minimize the effect on communities and the environment.
Long-term stability
A deactivated/decommissioned pipeline has a very long remaining life as a load-bearing structure. This reduces the risk of soil stability issues, and avoids major construction activities required to remove the pipe.
Now that you've explored what we do to safely plan, build, operate and maintain our pipelines, learn the various ways Enbridge works to ensure safety for the communities near our operations.