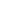Energy security is vital
Enbridge plays multiple key roles in North America's energy value chain—including oil and gas transportation via pipelines like Line 5, storage, gas distribution and renewable power generation—helping to secure energy security for all of us. Click on this link, or the image above, for a larger version illustrating the energy value chain and the work Enbridge does to support it.
Line 5 plays a key role
June 2, 2021
Until they experience disruption to their air conditioning, heat or power, the true meaning of energy security does not rise to the priority of the day for most people.
Energy security is having reliable and affordable access to energy sources, including solar, wind, oil, natural gas, and electricity. While the definition of energy security might be simple, the implications surrounding it can be complex.
Energy markets are vulnerable to a range of risk factors, including natural disasters, technical and supply chain issues, worldwide political tensions, and the ability of America’s energy systems to withstand unplanned disruptions. The topic of energy security rose to the forefront again when prices at the pump soared recently because a cyberattack shut down a pipeline that supplies oil to 14 states.
Pipelines like Line 5 help us withstand disruptions
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), the U.S. became the world's top crude oil producer in 2018, retaining that position through 2020. It produces approximately 20 percent of the world’s oil supply. The U.S. also is the largest producer of natural gas, and both energy sources are critical to building the foundation for renewable energy.
“As society transitions to a lower carbon economy, maintaining access to reliable, affordable and ever cleaner energy will be essential,” said Enbridge’s Chief Sustainability Officer Pete Sheffield.
“In the Great Lakes region, Line 5 provides critical support to the region’s economic vitality and energy security.”
Investing in the future
For Enbridge, energy security means investing in infrastructure that fosters diverse types of energy, designing redundancies throughout its energy network across North America.
“A focus on the efficient delivery of American made oil and natural gas helps to support economic recovery and energy security,” said Sheffield. “And as Enbridge continues investing to maintain and modernize our existing energy infrastructure, we’re also pursuing projects and investments that contribute to a lower carbon future.”
As such, Enbridge has invested since 2002 nearly $8 billion in renewable projects, including wind and solar farms, renewable natural gas and hydrogen. Enbridge also has invested more than $100 million in the last two years to implement successful measures in the Straits that help keep Line 5 operating safely and reliably.
Great Lakes Tunnel is a long-term solution
“Maintaining and strengthening energy infrastructure is an important aspect of energy security,” said Mike Moeller, Enbridge’s director of operations for the Great Lake region. “Michiganders and neighboring states have relied on the safe operation of Line 5 in the Straits for more than 65 years, and construction of the Great Lakes Tunnel will enhance operational and environmental protections of Line 5. The tunnel to encase a replacement section of Line 5 and essentially eliminate an anchor strike or spill in the Straits delivers to the region an additional layer of energy security.”
Enbridge has committed $500 million to build the Great Lakes Tunnel Project. The Great Lakes Tunnel will house a replacement section of Line 5 deep below the lakebed, virtually eliminating the chance of an anchor strike or spill.